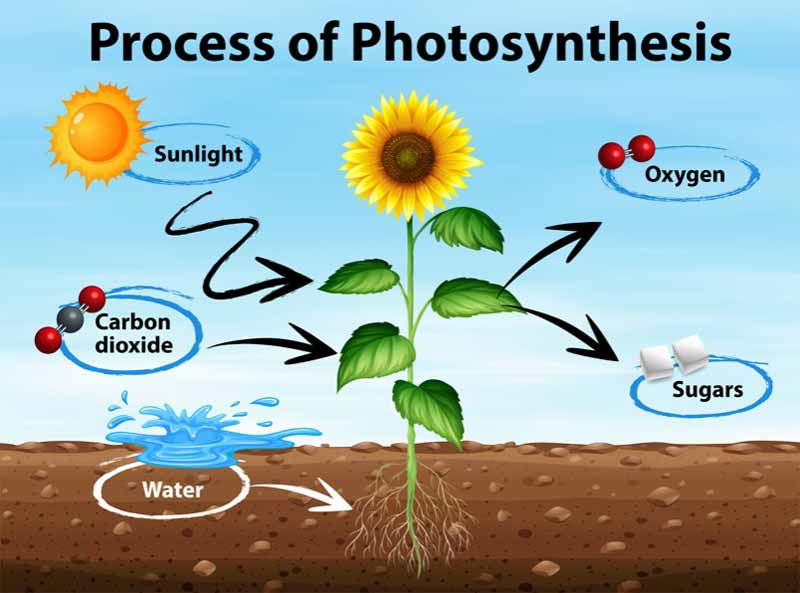
Plants are called producers because they are able to create their own food. through the process of photosynthesis, they convert light energy into organic matter.
This process allows plants to produce their own food, as well as oxygen gas, which is necessary for animal life.
Animals, on the other hand, must rely on producers for their food. They cannot convert light energy into organic matter and must eat plants or other animals to obtain the nutrients they need to survive.
While plants are the primary producers in most ecosystems, there are some environments, such as hydrothermal vents, where bacteria are the primary producers.
These bacteria are able to convert the chemical energy released by the vents into organic matter, which supports the entire vent ecosystem.
Plants are called producers because they produce their own food through photosynthesis.
In this process, they convert light energy into organic matter, as well as oxygen gas, which is necessary for animal life.
Animals cannot convert light energy into organic matter and must eat plants or other animals to obtain the nutrients they need to survive.
Table of Contents
How do plants produce oxygen?
Plants produce oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis. The process of photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen. Oxygen is released as a waste product and is used by animals to breathe.
The role of oxygen in plants is to provide them with the energy they need to grow. Plants use sunlight to create glucose from carbon dioxide and water.
The process of photosynthesis releases oxygen as a by-product. Plants need oxygen for respiration, which is a process that uses oxygen to convert glucose into energy.
Oxygen is also used by animals to breathe. When animals breathe in, they take in oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide.
Plants use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, so this exchange of gases between plants and animals is necessary for both to survive.
How does carbon dioxide help plants produce food?
Plants produce oxygen gas as a by-product of photosynthesis, which is the process that uses sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and other organic molecules.
Glucose is then used by plants to produce energy in the form of ATP, and it is also stored in plant cells for later use.
Carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis because it is one of the reactants used in the light-dependent reactions, which are necessary for the overall process.
In these reactions, sunlight energy is used to split water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen.
The oxygen gas produced is released into the atmosphere, while the hydrogen ions are used to convert carbon dioxide into organic molecules such as glucose.
Without carbon dioxide, plants would not be able to produce food through photosynthesis.
What are some examples of producers in the natural world?
Producers in the natural world come in all shapes and sizes, from tiny plankton to towering redwoods. But what all producers have in common is a capacity to create life from nothing.
- Producers are essential for creating and sustaining life on Earth. The food chain would not exist without them, and neither would we.
- Producers use photosynthesis to turn sunlight into energy, which they use to create organic molecules from simple inorganic molecules. This process is called carbon fixation .
- Some producers are autotrophs , which means they can create their own food source from scratch; others are heterotrophs , which means they must eat other organisms to survive.
- Nearly all producers are able to reproduce, and some can do so asexually as well as sexually .
- Producers are an important food source for consumers , which is why many are harvested by humans . We depend on producers for our very survival.
- Some producers, such as algae and bacteria , live in water; others, such as plants , live on land. There are even producers that live in the air!
- Producers come in all shapes and sizes, from tiny plankton to towering redwoods.
- Producers play a vital role in the global carbon cycle , helping to regulate the Earth’s climate .
- Producers are essential to life on Earth, and we depend on them for our survival.
What is photosynthesis and what role does it play in plant growth
Photosynthesis is the process that produces organic molecules from simple inorganic molecules from the sun’s energy and carbon dioxide.
The light energy liberates electrons from water molecules which combine with CO 2 to form C 6 H 12 O 6 (glucose).
Glucose is a basic food for plants, and it is used to produce other complex carbohydrates, such as cellulose, or stored as starch. This all occurs within the chloroplasts of photosynthetic cells.
The light energy also powers the synthesis of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the cell’s energy currency.
The Calvin cycle uses the ATP and glucose to produce more complex organic molecules, such as lipids and proteins.
So, photosynthesis is essential for plant growth because it provides the food and energy that plants need to grow and thrive.
Sunlight hits the leaves of a plant and is converted into chemical energy by chlorophyll molecules in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts.
This process is called photolysis. In photolysis, water molecules are split into oxygen gas (O2) and hydrogen ions (H+). The hydrogen ions combine with CO 2 to form glucose in a process called the carbon fixation cycle, also known as the Calvin cycle.
The light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis
There are two parts to photosynthesis: the light-dependent and light-independent reactions. The light-dependent reactions occur when light hits the plant, and the light-independent reactions occur when the plant is dark.
The light-dependent reactions use light energy to split water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen. The hydrogen is used in the light-independent reactions to make glucose from carbon dioxide.
The light-independent reactions do not need light to occur, but they do need the products of the light-dependent reactions (hydrogen and oxygen).
The light-independent reactions use the hydrogen and oxygen to make glucose from carbon dioxide.
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages: the light-dependent stage and the light-independent stage.
In the light-dependent stage, pigment molecules absorb energy from sunlight. This energy is used to split water molecules into hydrogen ions and electrons.
The electrons are passed through an electron transport chain, which generates ATP (adenosine triphosphate). ATP is used in the light-independent stage to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
In the light-independent stage, the hydrogen ions and electrons from the light-dependent stage are used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
This process does not require sunlight, but it does require ATP. The light-independent reactions are also known as the dark reactions or the Calvin cycle.
The light-dependent and light-independent reactions are both necessary for photosynthesis to occur.
The light-dependent reactions need sunlight to generate ATP, and the light-independent reactions need ATP to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
How plants produce glucose from carbon dioxide and water
Plants produce glucose from carbon dioxide and water through the process of photosynthesis. In photosynthesis, light energy is converted into organic matter, such as glucose. The light energy liberates electrons from water molecules which combine with CO2 to form O2 in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
The light energy liberates electrons from water molecules which combine with CO2 to form O2 in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
This is how plants produce glucose from carbon dioxide and water.
The benefits of photosynthesis for humans and the environment
Photosynthesis is a process that occurs in the leaves of green plants. During photosynthesis, light energy is converted into chemical energy, which is used to produce glucose from carbon dioxide and water.
The glucose produced by photosynthesis is then used by plants to produce cellulose and other important plant products.
Photosynthesis is an essential process for the survival of both plants and humans.
In addition to providing food for plants, photosynthesis also produces oxygen gas, which humans need to breathe.
The benefits of photosynthesis for humans and the environment are many. For humans, photosynthesis provides the food that we eat.
Plants produce glucose during photosynthesis, which is used to create cellulose and other important plant products. These products are then consumed by humans, providing us with the nutrients we need to survive.
The importance of photosynthesis extends beyond just human survival. This process is also responsible for the production of oxygen gas, which is required by all aerobic organisms (including animals) to breathe.
Photosynthesis thus plays a vital role in the global oxygen cycle, which is essential for the survival of all life on Earth.